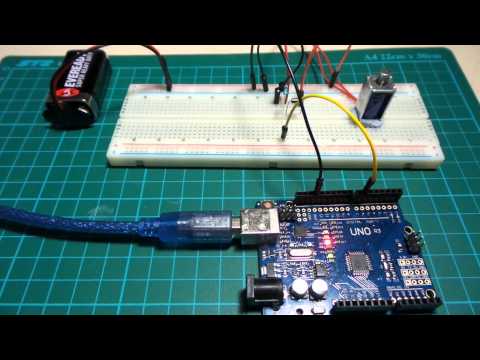
#102 SolenoidControl
Controlling a mini solenoid with an Arduino.

Here’s a quick demo of the circuit in action:
Notes
Solenoids are useful devices for converting electrical signals and digital logic into physical movement. Whereas motors provide rotation, solenoids are usually used for binary control (valves on or off, locks engaged or free).
So we basically need the Arduino to be a switch. Connecting an Arduino to a solenoid just requires attention to two factors:
- the current (and possibly voltage) required by the solenoid probably exceeds the power an Arduino can directly provide, so we’d use a transistor or FET to switch a higher-power current source
- being electromagnetic devices, solenoids can produce significant back-EMF and require a flyback diode to protect other components in the circuit
For this circuit, I’m using a mini push-pull solenoid that is rated for 3-12V. The data I have from the seller page on aliexpress specifies:
- Length: 20.3 MM
- Weight: 12g
- Voltage: DC 3 V, current: 0.08 A
- voltage: 6 V, Current: 0.17 A
- voltage: 9 V, Current: 0.26 A
- Voltage: 12v, current: 0.35 A
- Internal resistance: 32.8 ohm
That kind of makes sense, although I’m not sure why the rated current is a tad under the voltage/resistance calculation.
The switching transistor used here is the S9013, which is rated for 500mA continuous collector current - sufficient for this application. A 1N4001 diode provide flyback protection.
Construction



Credits and References
- Arduino Cookbook - 8.6. Controlling Solenoids and Relays
- Mini push-pull solenoids on aliexpress - 3-12V
- S9013 datasheet
- 1N4001-1N4007 datasheet