#387 GpsBasics
Using a NEMA-compatible GPS module for time and location with an Arduino.
Notes
The GPS module I obtained (similar to this) is variously marketed as GY-NEO6MV2 or GY-GPS6MV2, and at least in my case uses an integrated GPS chip/module marked as XM37-1612.
GPS Module
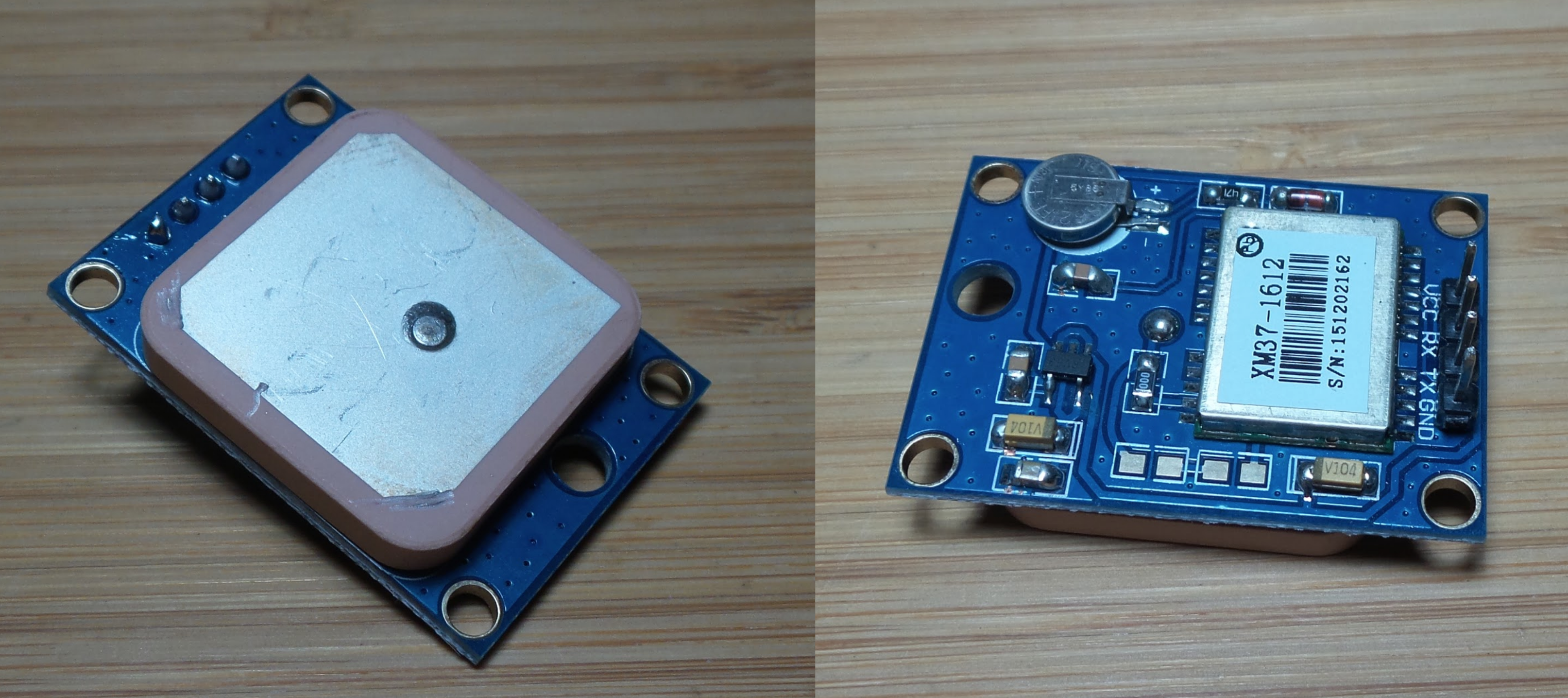
Specifications (as far as I’ve been able to glean from the Internet):
- Communication mode: TTL level, compatible with 3.3v / 5v system
- Power supply: DC 2.7-5v
- Working current: 45mA
- txd rxd impedance: 510R
- Default transmission speed: 9600
- Time to catch: warm start: 1s
- Cold start: 27s
- Temp: -40 ~ 85 ℃
- Positioning accuracy: 5m
- Module size: 25 mm x 35 mm (approximately)
- Antenna size: 25 mm x 25 mm
Features:
- use the XM37-1612 module. MTK platform, with high gain active antenna
- TTL level, compatible with the 3.3v / 5v system
- the default baud rate: 9600
- with rechargeable backup battery, can save the ephemeris data when it power off, and make the boot warm.
- Suitable for RC Quadcopter, Browser
Listening to Raw GPS Module Output
The module has basic serial RX/TX connectors, that runs at 9600 baud.
To examine the raw output, here I’m connecting directly to the module with a
CH340G-based USB to UART adapter,
and using screen to display the output.
On MacOSX, the programmer shows up as a character device:
$ ls -1 /dev/cu*
/dev/cu.Bluetooth-Incoming-Port
/dev/cu.Bluetooth-Modem
/dev/cu.usbmodem1412
/dev/cu.wchusbserial14530 # <- this one (it appeared after connecting the module)
The simplest way of getting connected on MacOSX is to use screen, at 9600 baud:
$ screen /dev/cu.wchusbserial14530 9600
..
$GPGSV,2,1,07,21,60,325,26,24,44,039,33,20,35,016,19,29,31,191,37*7B
$GPGSV,2,2,07,31,10,212,20,193,,,,25,,,16*75
$GPRMC,194319.000,A,0123.0961,N,10350.3533,E,0.11,304.12,050518,,,A*6B
$GPVTG,304.12,T,,M,0.11,N,0.20,K,A*3B
$GPGGA,194320.000,0123.0964,N,10350.3532,E,1,4,2.09,135.6,M,3.9,M,,*6E
$GPGLL,0123.0964,N,10350.3532,E,194320.000,A,A*5F
$GPGSA,A,3,24,29,31,21,,,,,,,,,2.30,2.09,0.96*0B
$GPGSV,2,1,07,21,60,325,26,24,44,039,33,20,35,016,19,29,31,191,37*7B
$GPGSV,2,2,07,31,10,212,19,193,,,,25,,,16*7F
$GPRMC,194320.000,A,0123.0964,N,10350.3532,E,0.14,333.89,050518,,,A*66
$GPVTG,333.89,T,,M,0.14,N,0.26,K,A*3E
$GPGGA,194321.000,0123.0967,N,10350.3530,E,1,4,2.09,135.3,M,3.9,M,,*6B
$GPGLL,0123.0967,N,10350.3530,E,194321.000,A,A*5F
$GPGSA,A,3,24,29,31,21,,,,,,,,,2.30,2.09,0.96*0B
$GPGSV,2,1,07,21,60,325,26,24,44,039,33,20,35,016,19,29,31,191,37*7B
$GPGSV,2,2,07,31,10,212,18,193,,,,25,,,16*7E
$GPRMC,194321.000,A,0123.0967,N,10350.3530,E,0.20,338.91,050518,,,A*63
$GPVTG,338.91,T,,M,0.20,N,0.38,K,A*34
$GPGGA,194322.000,0123.0969,N,10350.3529,E,1,4,2.10,134.9,M,3.9,M,,*6D
$GPGLL,0123.0969,N,10350.3529,E,194322.000,A,A*5A
$GPGSA,A,3,24,29,31,21,,,,,,,,,2.31,2.10,0.96*02
$GPGSV,2,1,07,21,60,325,26,24,44,039,33,20,35,016,19,29,31,191,37*7B
$GPGSV,2,2,07,31,10,212,18,193,,,,25,,,17*7F
$GPRMC,194322.000,A,0123.0969,N,10350.3529,E,0.29,324.39,050518,,,A*60
$GPVTG,324.39,T,,M,0.29,N,0.53,K,A*3F
$GPGGA,194323.000,0123.0973,N,10350.3524,E,1,4,2.09,134.4,M,3.9,M,,*6F
$GPGLL,0123.0973,N,10350.3524,E,194323.000,A,A*5D
$GPGSA,A,3,24,29,31,21,,,,,,,,,2.30,2.09,0.96*0B
$GPGSV,2,1,07,21,60,325,26,24,44,039,33,20,35,016,19,29,31,191,37*7B
$GPGSV,2,2,07,31,10,212,18,193,,,,25,,,17*7F
$GPRMC,194323.000,A,0123.0973,N,10350.3524,E,0.37,315.44,050518,,,A*60
$GPVTG,315.44,T,,M,0.37,N,0.68,K,A*30
$GPGGA,194324.000,0123.0977,N,10350.3519,E,1,4,2.09,133.9,M,3.9,M,,*68
$GPGLL,0123.0977,N,10350.3519,E,194324.000,A,A*50
$GPGSA,A,3,24,29,31,21,,,,,,,,,2.30,2.09,0.96*0B
$GPGSV,2,1,07,21,60,325,26,24,44,039,33,20,35,016,19,29,31,191,37*7B
$GPGSV,2,2,07,31,10,212,18,193,,,,25,,,18*70
$GPRMC,194324.000,A,0123.0977,N,10350.3519,E,0.46,311.79,050518,,,A*61
..
The NEMA Protocol
This module appears to be constructed with a boot-time configuration:
- Protocol: NMEA, Input/output, ASCII, 0183, 2.3 (compatible to 3.0)
- Messages: GSV, RMC, GSA, GGA, GLL, VTG, TXT
- Baud rate: 9600
The NEMA protocol is apparently one of those nasty proprietary and copyrighted standards, intended for Serial-Data Networking of Marine Electronic Devices. The full NMEA Standards are priced way beyond the reach of a weekend tinkerer. But happily there is enough information floating around the net to at least make sense of the messages coming out of NEMA-compatible products.
With the help of Glenn Baddeley’s GPS - NMEA sentence information site, I can make some sense out of the trace captured above. For example:
$GPGSV,2,1,07,21,60,325,26,24,44,039,33,20,35,016,19,29,31,191,37*7B
$GPGSV,2,2,07,31,10,212,18,193,,,,25,,,17*7F
$GPRMC,194322.000,A,0123.0969,N,10350.3529,E,0.29,324.39,050518,,,A*60
$GPVTG,324.39,T,,M,0.29,N,0.53,K,A*3F
$GPGGA,194323.000,0123.0973,N,10350.3524,E,1,4,2.09,134.4,M,3.9,M,,*6F
$GPGLL,0123.0973,N,10350.3524,E,194323.000,A,A*5D
$GPGSA,A,3,24,29,31,21,,,,,,,,,2.30,2.09,0.96*0B
Here we have a number of $GPxxx sentences:
- $GPGSV - GPS Satellites in View
- $GPRMC - Recommended Minimum Specific GPS/TRANSIT Data
- $GPVTG - Track Made Good and Ground Speed
- $GPGGA - Global Positioning System Fix Data
Followed by interpreted sentences from the GPS unit:
- $GPGLL - Geographic position, latitude / longitude
- $GPGSA - GPS DOP and active satellites
Using NEMA GPS Data on an Arduino
The TinyGPSPlus library parses the NEMA codes and provides a nice API for getting the results. It can work in conjunction with SoftwareSerial library to allow GPS serial connections on pins other than 0/1.
Code
The GpsBasics.ino sketch is a simple demonstration, heavily influenced by the TinyGPSPlus examples.
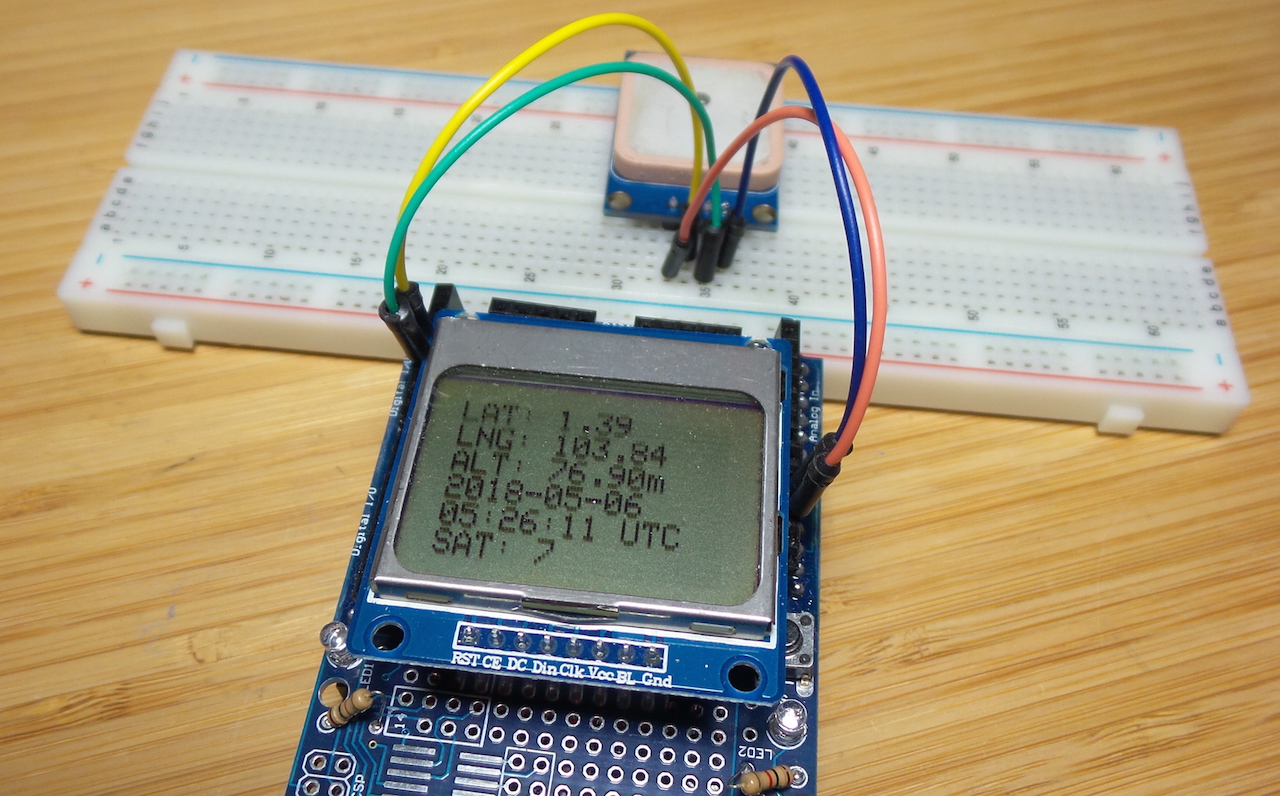
I’m using an Arduino with Nokia 5110 Shield, so in addition to logging detailed GPS readings to the serial port, it displays the basic time and location information on the LCD.
Libraries Used
- TinyGPSPlus - for decoding NEMA data
- SoftwareSerial - to communicate with the GPS module on arbitrary pins
- SPI - LCD communciations
- Adafruit_GFX - LCD graphics support
- Adafruit_PCD8544 - LCD display driver
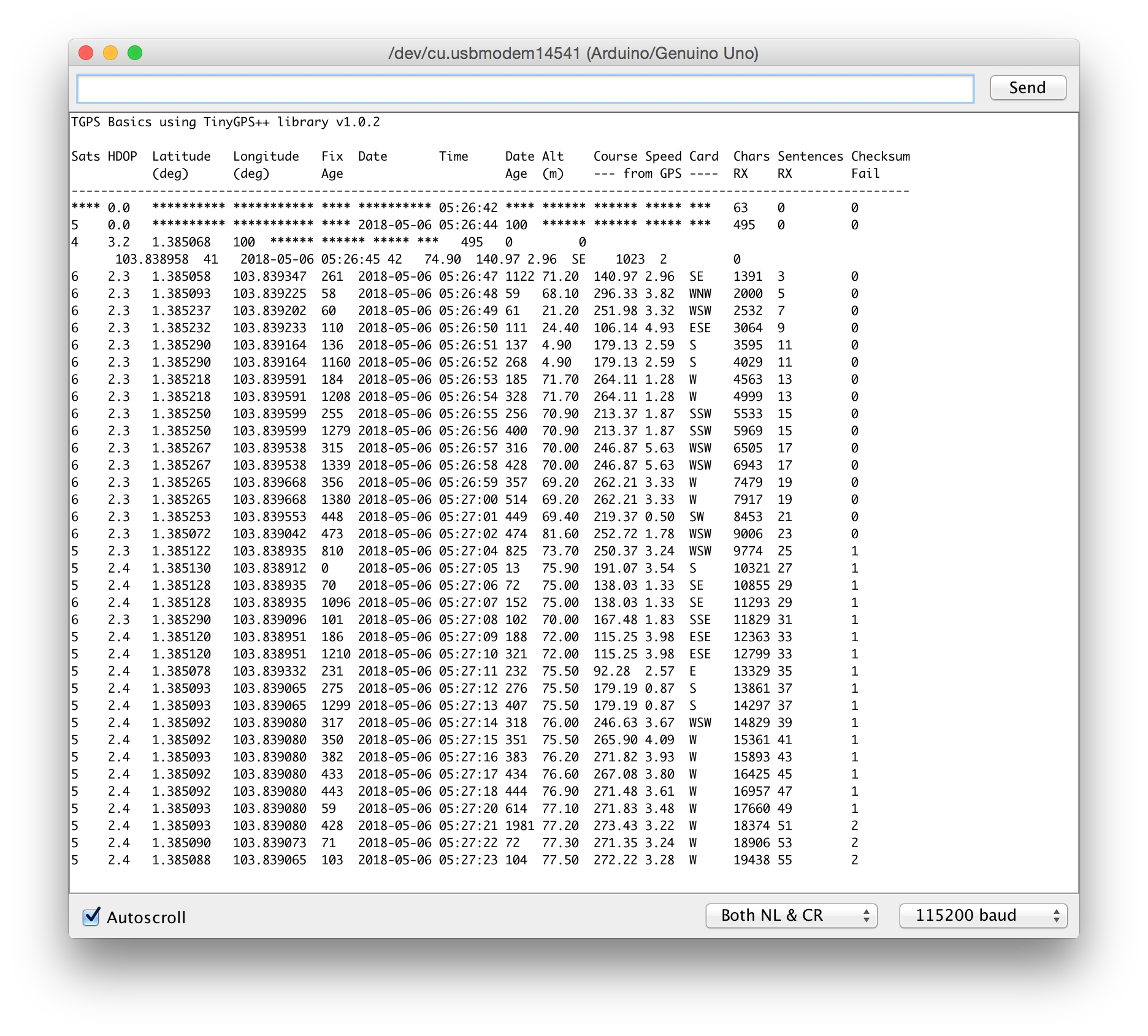
Output
A summary is displayed on the LCD:

And details logged to serial output:
Construction
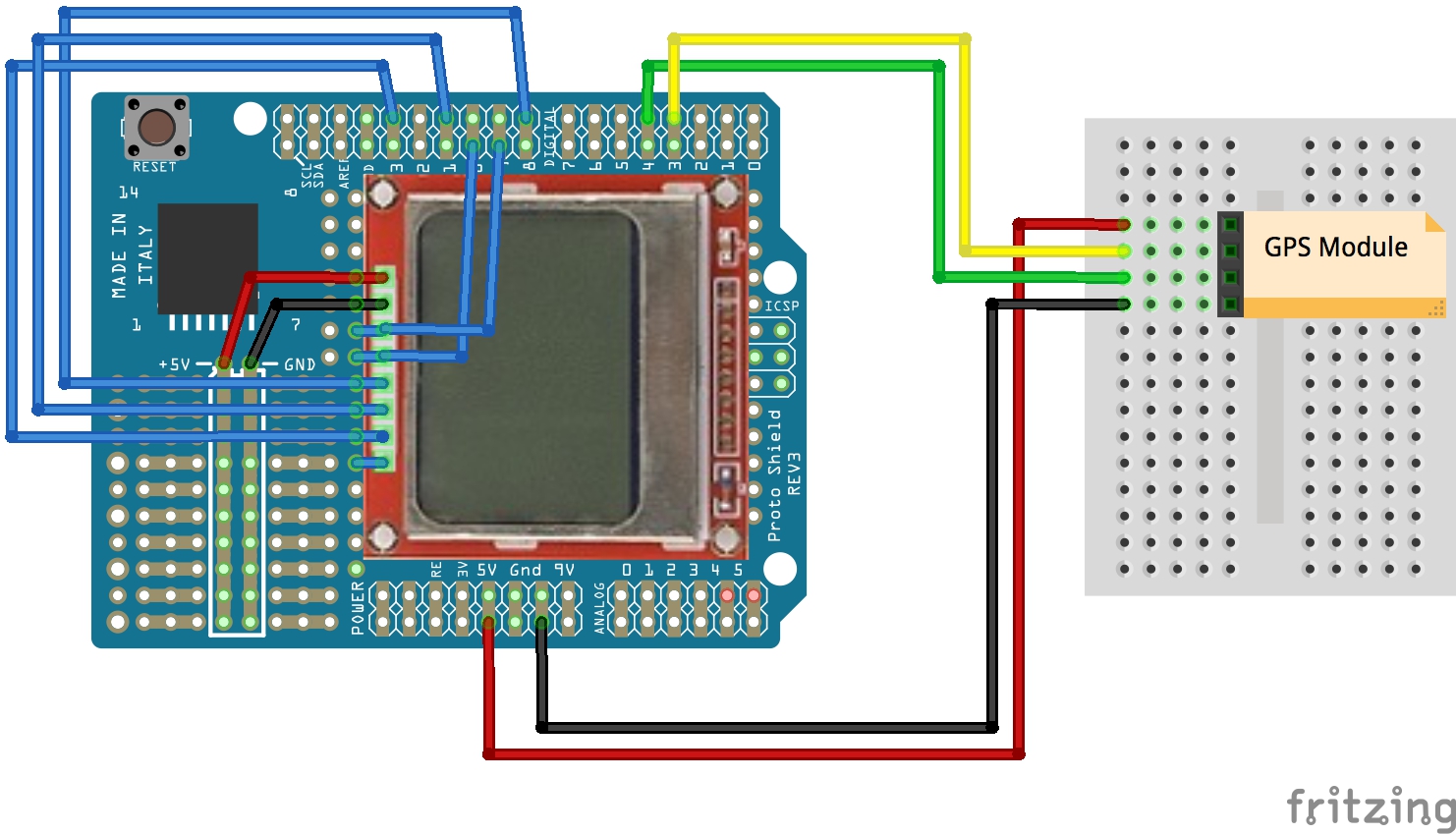
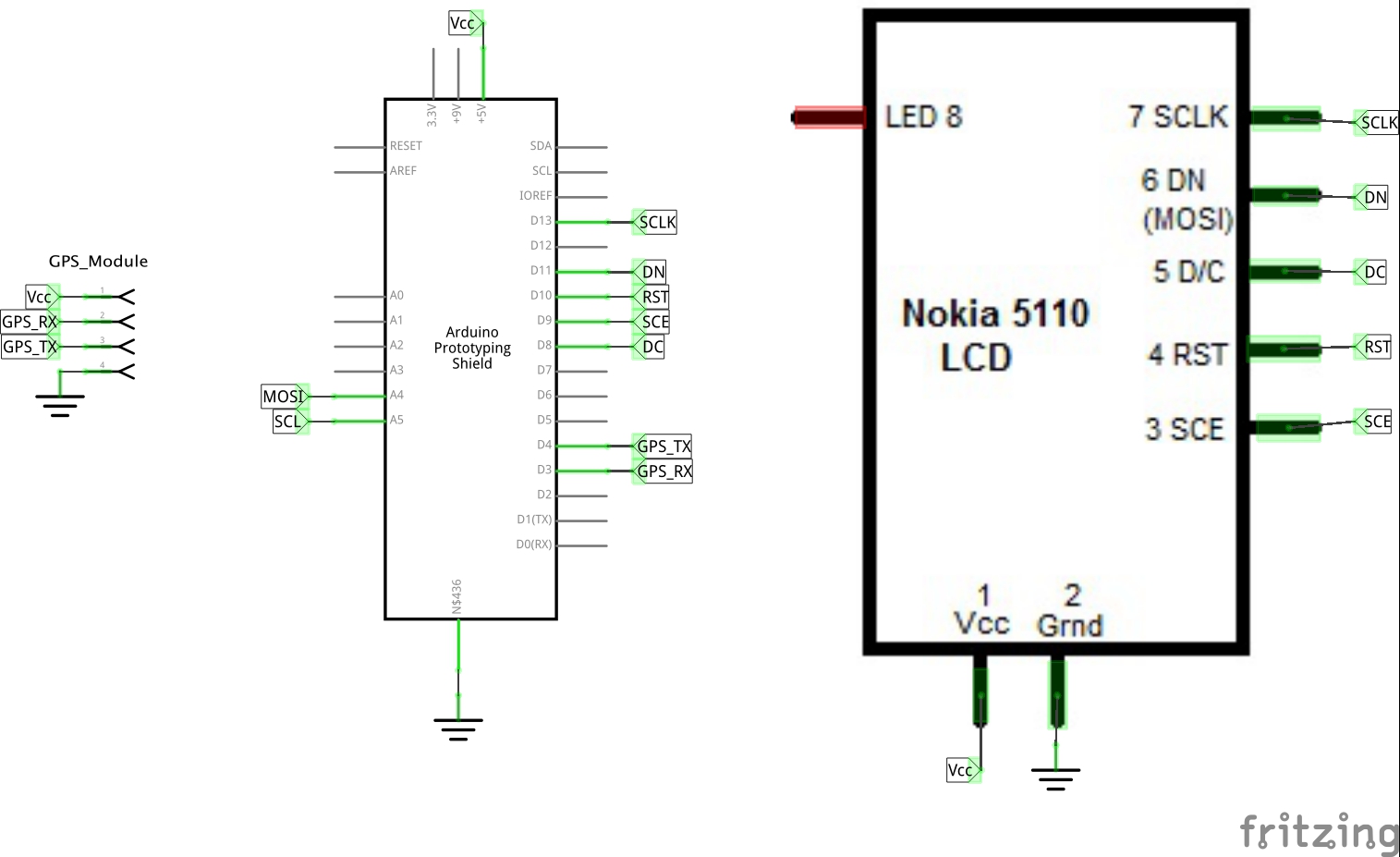
Pin Connections
| Module | Schematic Label | Arduino | Script Label |
|---|---|---|---|
| VCC | VCC | 5v | - |
| GND | GND | GND | - |
| TXD | GPS_TX | 4 (RX) | GPS_RX_PIN |
| RXD | GPS_RX | 3 (TX) | GPS_TX_PIN |
Credits and References
- LEAP#377 Nokia 5110 Shield
- Ublox GY-NEO6MV2 GPS Module - from seller on aliexpress
- GY-NEO6MV2 GPS Module - similar device, with datasheet available
- TinyGPSPlus - customizable Arduino NMEA parsing library
- SoftwareSerial
- Using a GPS receiver for Arduino - useful blog post by Sander van de Velde
- 6.14. Getting Location from a GPS - from the Arduino Cookbook
- NMEA data - great background on NEMA data
- GPS - NMEA sentence information - Glenn Baddeley
- NMEA Standards
- ..as mentioned on my blog
