#013 NOT Gate with Resistor-Transistor Logic
Test the basic resistor-transistor logic NOT gate (inverter)
Here’s a quick video of the circuit in action:
Notes
Resistor–transistor logic (RTL) is a class of digital circuits built using resistors as the input network and bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) as switching devices. RTL is the earliest class of transistorized digital logic circuit and is largely obsolete now.
It is interesting to see how various logic gate may be realised with BJTs and resistors alone. Here is the basic inverter gate.
| IN | OUT |
|---|---|
| 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 |
The circuit uses a digital output pin as the input to the inverter. The output is tapped at the collector of the transistor. The output voltage is read with an analog input pin, and the value is echoed to the Arduino serial port.
The Arduino is not really a core part of the circuit. It only does the following:
- provides +5V power supply (for convenience)
- automates the toggling of the driving input
- measures the input and output voltages for plotting
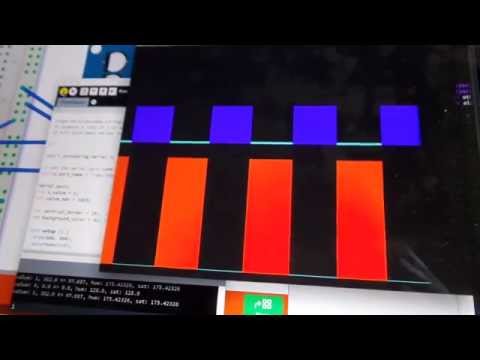
Here’s a sample trace. The lower trace is the signal input, and the upper trace is the output of the inverter.

We clearly lose significant voltage at the output because of the current-limiting resistors. There is also noticable noise in the output, mainly because the circuit is so simple it lacks any attempt at smoothing the source voltage or output. These would be significant issues when cascading the inverter output to subsequent logic blocks.
Construction



Credits and References
- Resistor-Transistor Logic - wikipedia page
- 2N3904 datasheet - the NPN used in this circuit
- Logic NOT Gate Tutorial - explains of the basic circuit used here.
- The NOT gate - describes a practical implementation of a “real” inverter circuit
- Logic Gates using Transistors
- Transistor AND, OR, NAND, NOR Gates